Types of AI in the education context
To help you learn more about what AI tools can do in the educational context, we have compiled a list of different types of tools in use. The list aims to exemplify some of the thousands of tools available.
Search and find
On the website theresanaiforthat.com you can search among thousands of AI tools sorted by task.
What do we actually mean when we talk about and exemplify AI tools? Actually, AI is woven into our everyday life in a way that we don't always notice, and we have been relying on AI for a long time. It is not always obvious that we are using AI because AI is increasingly used. The examples Educate includes on this page specifically describe tools that can be used to solve common tasks in an academic education context. The examples are not recommendations.
ChatGPT
Perhaps the most notorious AI tool at the moment. ChatGPT can generate text-based answers to questions and complete tasks in a very short time. The example shows the free version of ChatGPT answering an exam question that requires higher order thinking skills such as analysis, comparison, application of facts and similar reasoning. The tool can be used with input and output in most languages.
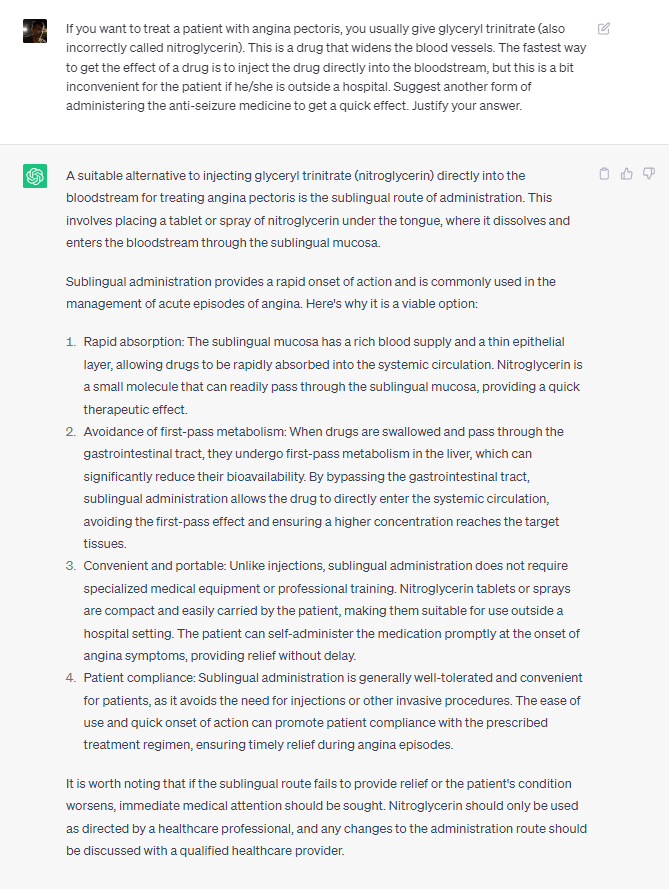
Example from exam in Fysikalisk kemi med galenisk farmaci (Physical chemistry with galenic pharmacy) 7,5hp, semester 2 (LNU), public record
Examples of AI in an education context
AI and information search
Currently, AI tools are limited in their functionality in the information retrieval process. However, AI can be utilised to find relevant search terms within a topic.
When working academically, it is crucial to find, review, and use different types of sources. Knowing where the information comes from is important to assess its credibility. Hence, AI not providing correct references is unsuitable in the information retrieval context
Approach when using AI tools in the information retrieval process
- It is important to encourage students to evaluate their search results to ensure they meet the requirements of the assignment.
- Students must verify facts, figures, quotes, and data using credible sources to ensure the information is accurate.
- Students are always responsible for what they create using AI. In the methods section (or equivalent), they should describe how they used the tool. Both the AI tool's name and prompt should be included. The generated response can then be attached as an appendix.
AI and literature reviews
AI tools are not yet suitable for conducting literature reviews, as the method is based on transparency and reproducibility. However, AI tools can be used to identify keywords and gain a better understanding of the topic.
Contact the University Library if you're interested in integrating AI and information search into your course: biblioteket@ju.se.
References
AI for Education. (2023). How to use IA responsibly every time. https://www.aiforeducation.io/ai-resources/how-to-use-ai-responsibly-every-time
McAdoo, T. (2023, April 7). How to cite ChatGPT. APA Style. https://apastyle.apa.org/blog/how-to-cite-chatgpt
Summary, phrasing and structure
In addition, AI tools can help paraphrase, summarise and compare scientific articles. They can analyse and extract relevant and important information from multiple sources, allowing students or researchers to compile information effectively. This helps in writing literature reviews and producing well-structured text. AI tools such as Grammarly and QuillBot can provide suggestions on how to improve spelling, grammar, phrasing and structure. These tools can also generate text to finalise or improve what has already been written.
Data analysis
AI tools can interpret and analyse data. They can process large amounts of data, identify patterns and generate insights. For example, AI-powered analytics tools can perform statistical analysis, visualise data and make predictions.
The tools mentioned above can be of great help to students, teachers and researchers. At the same time, an understanding of how the tools work is needed to understand how they can be used. It is also important for teachers to understand how the tools work, so that they understand the consequences of allowing or restricting their use in teaching and examination.
Examples of the use of AI in everyday life
- Autonomous vehicles: AI plays a crucial role in self-driving cars. Sensors and cameras collect data about the environment, and AI algorithms process this data to make real-time decisions, such as detecting objects, recognising traffic signs and navigating the vehicle safely.
- Fraud detection: AI is widely used in financial systems to detect fraudulent activities. Machine learning algorithms analyse large amounts of data, such as transaction history, purchase patterns and user behaviour, to identify anomalies and potentially fraudulent transactions, thereby preventing financial losses.
- Image and speech recognition: AI-powered image and speech recognition technologies are used in various applications and devices. These technologies enable automatic tagging of photos on social media, facial recognition for unlocking smartphones, voice commands for virtual assistants and even real-time language translation.
- Personalised recommendations: Online platforms such as streaming services, e-commerce websites and social media platforms use AI algorithms to analyse your browsing history, purchase history and interactions to provide personalised recommendations. These recommendations are based on patterns and preferences learnt from your data and the data of similar users.
- Voice assistants: Voice-activated AI assistants such as Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant are common in smartphones, smart speakers and other devices. They use natural language processing and machine learning to understand and respond to voice commands, perform tasks such as setting reminders, playing music, answering questions and controlling smart home devices.
- Spam filters: Email services use AI algorithms to filter out spam messages from your inbox. These filters learn from patterns and characteristics of spam messages, such as keywords, senders and email structures, to identify and block unwanted and potentially harmful messages.
- Virtual customer support: Many companies use AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants to handle customer enquiries and provide support. These chatbots can understand and respond to customer questions, make recommendations and provide basic assistance, reducing the need for human intervention.